Introduction
Congo is the world’s second-largest rainforest located on the African continent. As we all obviously know, the first one is the great Amazon rainforest in South America. Congo rainforest has spread throughout the 500 millions of acres in Africa which is nourished by the majestic Congo River. It is formally known as Zaire River.
The Congo River is thought to have formed between 1.5 and 2 million years ago during the Pleistocene era. There are three main tributaries which feed the Congo River, including Aruwimi, Kasai and Lomami rivers. The origin of this River is mountains of the northwestern Tanganyika in Zambia and Nayasa lakes in Malawi state. This River’s catchment areas are eastern and central Africa and falling into the Atlantic sea at Western Africa. During the journey from east to west in Africa, Congo River passes the Earth’s equator two times as flowing zigzag pattern. In every second, River release 1.25 million cubic feet of water into the Atlantic Ocean.

Congo River is the second-longest channel in the African continent. It second to the Nile River, which is 6650 kilometres in length. However, Congo is the world 9th longest channel.
Location of the Congo River
This large River is flowing through the six countries including the Republic of Congo, Republic of central Africa, Zambia, Angola, Cameroon and Tanzania in Central Africa. This River disburses most problems associated with water scarcity in central Africa with a length of 4700 kilometres.
The Congo basin is margined on the south and west by the Atlantic Ocean, on the north by Sahara desert, and on the East by African lakes.
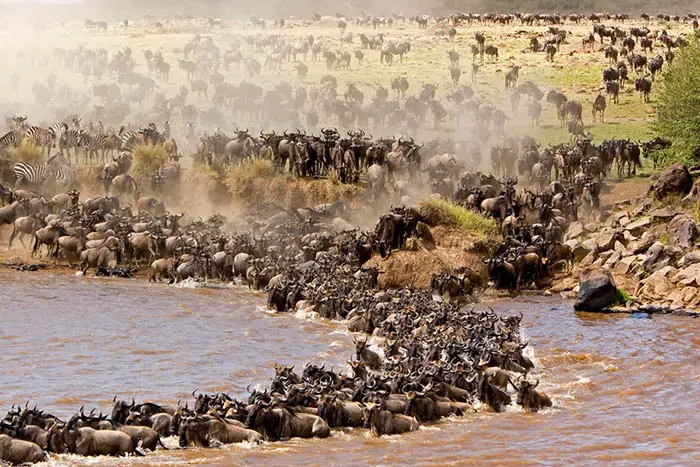
River Congo’s scattered drainage system supply food, water, medicines and transport for about 75 million people who live in the basin of the River.
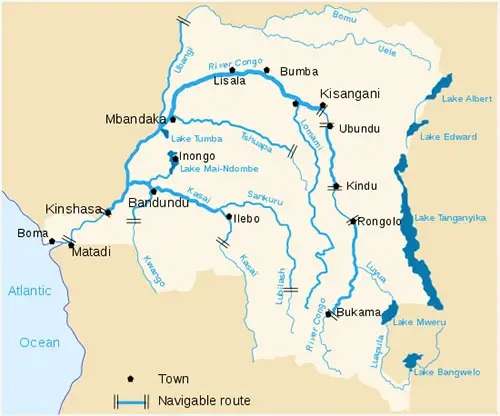
Topography of the Congo River
Congo River widens in some areas creating lake-like formations. These water bodies are high in-depth, which giving the world deepest River status for the Congo River. Maximum depth of the River is 220 meters. Therefore sunlight can’t penetrate to the river bottom of this deepest areas. So these areas are lack of green water plants.
If the Congo River turned eastern side from central Africa instead of flowing towards western Africa, it will meet the Indian Ocean after the flowing of 700 kilometres. If that happened then, this great River would not be able to give life to the billions of flora and fauna, and it would be a huge barrier to the progression of humankind.
Environment
The area where the Congo River flows down to the Atlantic Ocean is called the Congo River Basin. After the Amazon Basin, this Basin is the second largest River basin in the world, covering 3.4 million square kilometers. (Amazon River basin covers 7.5 million square kilometers.)
The Congo River basin is an extremely fertile ecosystem with small rivers, swamps and evergreen forests. That total area belongs to the countries that have mentioned above.
The Congo River Basin expands through the Earth’s equator. Therefore, equatorial climate dominates in the Congo basin. A large River with this warm tropical monsoonal climate, it forms the world second largest rainforest apart from the Amazon rainforest.

Life in the basin
The Congolese rainforest is home to millions of inimitable flora and fauna. According to the scientist’s research in this massive rainforest, it has counted more than 10,000 of tropical plant species. Nearly 30% of species out of that, cannot be identified anywhere in the world. Apart from that, it is home to 400 species of mammals, 1,000 species of birds about 700 species of fish and 2,040 species of butterflies. Most of them are endemic species for the region. Basin forest inhabit the threatened species of mammals including lowland and mountain gorillas, chimpanzees, and bonobos. Antelope species who are native to the Africa very common in the area.
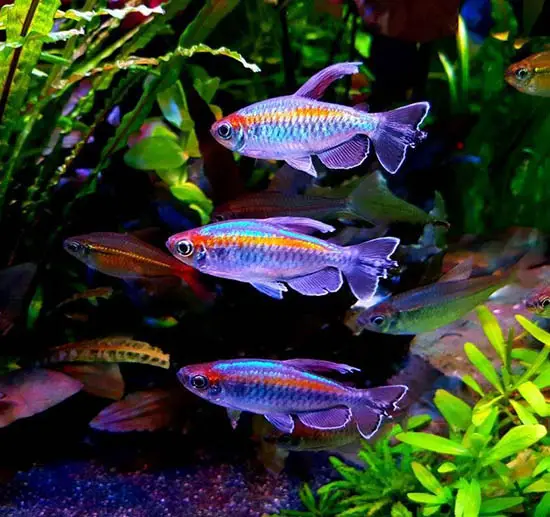
One of the main huge predator in the Congo River is African giant Tigerfish. Some electric eel species also live in the river. A well-known ornamental fish called Congo tetra found in the central region of the basin. They are a member of African tetra family. Some several species of turtles, dwarf crocodile, Nile crocodile and slender-snouted crocodiles native to the Congo basin.

Significance of the Basin
The Congo rainforest is an indispensable forest for carbon dioxide absorption from the atmosphere and oxygen production. Therefore Congo rainforest is famous as the second largest lungs on Earth following only the Amazon rainforest.
However Scientists have identified by a research carried out in Congo Basin, the trees in some parts of the area are losing their ability to fixing the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This will affect world health directly as greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide have linked to climate change. They believed as reasons for this adverse event is the global warming and drought retard the growth of rainforest trees. Therefore it weakened carbon uptake.
Congo River and Human
According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), humans have inhabited the basin region for about 50,000 years. Today, it is home to about 75 million people, including 150 ethnic groups and African tribes.

Congo River is consider as the one of important navigation system in Africa. Because it used to transport Copper production from Katanga to the coastal region in Democratic Republic of the Congo. About forty hydropower plants are generating electricity in basin using hydropower in the River. Researches have proven that potential for hydropower generation in the whole basin is estimated for 13% of global hydropower potential. There are a lot of upcoming planned hydroelectricity projects. However this would not be a sustainable solution for the environment of the basin. This may lead to extinction of the endemic and other sensitive species from the Africa.
The basin areas are famous for some sports activities including Congo river golf, and Congo river rapids ride at Busch Gardens.
Congo rainforest is degrading rapidly due to the clearing for small scale farming, hydro-power plants and logging. This adversely affects the native species by habitat fragmentation and loss of their territory. If the current deforestation rates continue, it will completely disappear the Congo rainforest at the end of this century. Research has found that within fifteen years between 2000-2015, Congo has lost an area which is similar to the total area of Bangladesh.







